By: CS2103T W11-3 Team Since: Feb 2019 Licence: MIT
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Additional Information
- 3. Quick Start
- 4. Features
- 4.1. Standardizing Command Formats
- 4.2. Seeking Help:
help - 4.3. Adding a Place:
add - 4.4. Listing All Places:
list - 4.5. Editing a Place:
edit - 4.6. Searching Places by Name:
search - 4.7. Searching places by Ratings:
searchr - 4.8. Searching Places by Tags:
searcht - 4.9. Searching places by Country:
searchc - 4.10. Searching Places by Year of Visit:
searchyear - 4.11. Deleting a Place:
delete - 4.12. Deleting Multiple Places:
deletem - 4.13. Selecting a Place:
select - 4.14. Listing Previously Entered Commands:
history - 4.15. Undoing Previous Command:
undo - 4.16. Redoing the Previously Undone Command:
redo - 4.17. Generating Charts:
generate - 4.18. Clearing All Entries:
clear - 4.19. Exiting the Program:
exit - 4.20. Saving of Data
- 5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- 6. Cheatsheet
1. Introduction
During your travels, have you ever wanted to curate all your travel moments, and wished there was an app to do just that? There were approximately 1.4 billion travelers in 2018 alone. That means 1 out of every 5 person on the planet is a traveler, you are certainly not alone in your struggles. Is there a solution to all your 21st century travel woes?
Introducing TravelBuddy. TravelBuddy is a desktop journal app that curates all your travel moments! Here are 4 ways to use TravelBuddy:
-
TravelBuddy Records: Helps you capture, store, organize and edit info about the places you’ve been to.
More info starting from here: Section 4.3, “Adding a Place:add” -
TravelBuddy Search: Helps you search through your list of places quickly to find what you were looking for.
More info starting from here: Section 4.6, “Searching Places by Name:search” -
TravelBuddy Photos: Helps you attach photos to your list of places.
More info here: Section 4.3.1, “Including a photo when adding a place withp/” -
TravelBuddy Analytics: Helps you gather insights into your travel patterns and behavior.
More info here: Section 4.17, “Generating Charts:generate”
Best of all, you can accomplish any of these tasks with just a single command. So, are you ready to redefine traveling?
2. Additional Information
Before continuing, it may be helpful to familiarize yourself these two symbols that you will encounter in this User Guide:
| This tells you there is important information that you should take note of. |
| This alerts you of useful tips and tricks that will improve your TravelBuddy experience. |
| This WARNING symbol is used to alert you of something critical. |
3. Quick Start
Here are the steps to get you started with using TravelBuddy:
-
Ensure you have Java version
9or later installed in your computer. The list of Java versions available for download can be found here. -
Download the latest version of TravelBuddy. The latest TravelBuddy jar file can be found here. Once the download is successful, you should be able to see a file named
travelBuddy.jar. -
Double-click
travelBuddy.jarto start the app. TravelBuddy’s Graphical User Interface (GUI) should appear in a few seconds, as shown in Figure 3.1.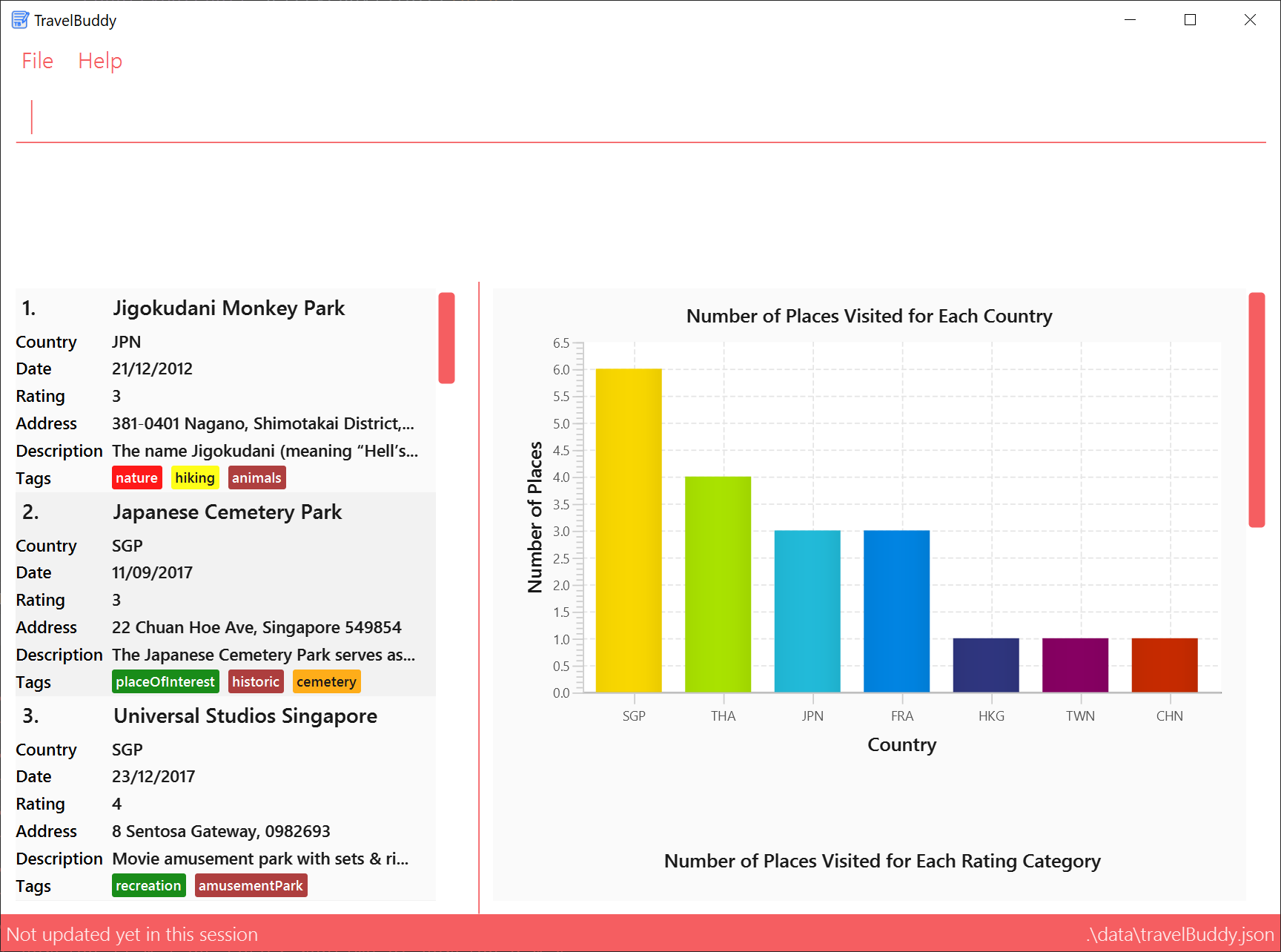 Figure 3.1: An illustration of how the TravelBuddy GUI looks
Figure 3.1: An illustration of how the TravelBuddy GUI looks -
Perform a quick test to verify that TravelBuddy works by typing in a command in the command box and press Enter to execute it.
Example: Type
helpand press Enter to open the help window.Below are other example commands you may try:
List all places
listAdds NUS Computing to the list of places
add n/NUS Computing cc/SGP dv/10/10/2018 r/5 d/No Description a/NUS School of Computing, COM1, 13 Computing Drive, 117417Deletes the 3rd place shown in the current list
delete 3Exits the application
exit -
For a detailed explanation of each command, refer to Section 4, “Features”.
-
For a complete summary of each command, refer to Section 6, “Cheatsheet”.
4. Features
4.1. Standardizing Command Formats
The following covers the standard format to be used for all the commands in TravelBuddy and the syntax that follows:
| The code in this section is merely for illustrative purposes. It is kept brief to highlight the formatting standards for all the commands and not the actual commands themselves. Do not copy and paste the commands in this section. |
-
Some commands may have a shortcut, which you can use to execute the command.
Example: Foradd, its shortcut isa. Hence, you can either typeadd n/Botanic Gardensora n/Botanic Gardens. -
Words in
UPPER_CASEare the parameters that you have to supply.
Example: Foradd n/NAME,NAMEis a parameter which can be substituted to beadd n/Botanic Gardens. -
Items in square brackets are optional.
Example: Foradd n/NAME [t/TAG], it can either be specified asadd n/Botanic Gardens t/facultyor asadd n/Botanic Gardens. -
Parameters can be in any order.
Example: If the command specifies the parametersn/NAME r/RATING, then changing the order tor/RATING n/NAMEis also acceptable. -
Whenever there are duplicate parameters, the last duplicated parameter is chosen.
Example: If the command isadd n/Singapore Zoo n/Botanic Gardens, where there are duplicates of then/NAMEparameters, the last parameter,n/Botanic Gardens, is chosen to be added to the list of places. -
Some parameters have a specific input format.
Example: Fordv/DATE_VISITED, theDATE_VISITEDneeds to follow theDD/MM/YYYYformat.
4.2. Seeking Help: help
Description: The help command opens up a help page.
Shortcut: he
Format: help
| The help page will be shown in another window, but you can resize and move it around. This can be useful to refer to when using the app. |
| A quick alternative way to seek help is to hit the F1 key. |
4.3. Adding a Place: add
Description: The add command adds a place to TravelBuddy.
Shortcut: a
Format: add [n/NAME] [cc/COUNTRY_CODE] [dv/DATE_VISITED] [r/RATING] [d/DESCRIPTION] [a/ADDRESS] [p/FILE_PATH]
[t/TAG]…
The Table 4.3.1 below shows the parameters that require a specific input format to be added.
Parameter |
Parameter Prefix |
Specific Input Format |
|
|
An integer ranging from |
|
|
A valid ISO-3166 three-letter country code |
|
|
A valid date that follows the |
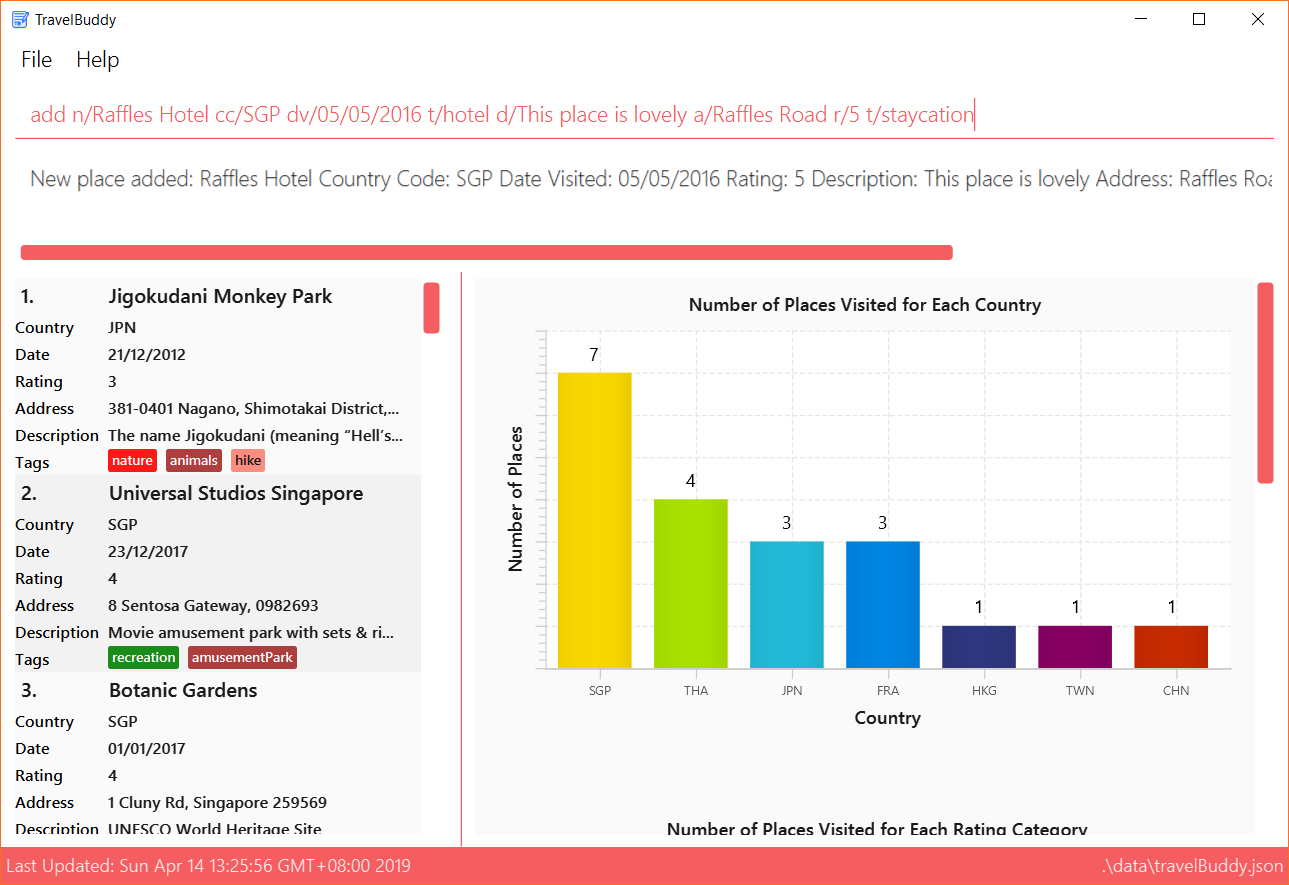
Examples: Given below are some examples on how to utilize the add command:
-
add n/Botanic Gardens cc/SGP dv/01/01/2017 r/4 d/UNESCO World Heritage Site a/1 Cluny Rd, Singapore 259569 t/nature
Adds Botanic Gardens to the list of places you have visited into TravelBuddy. -
add n/Raffles Hotel cc/SGP dv/05/05/2016 t/hotel d/This place is lovely a/Raffles Road r/5 t/staycation
Adds Raffles Hotel to the list of places you have visited into TravelBuddy.
Figure 4.3.1 below shows the outcome of a specific add command
| A place can have any number of tags (including 0 tags). |
4.3.1. Including a photo when adding a place with p/
Description: The add command can also attach a single photo
when adding a new place to TravelBuddy.
The photo must be an image file that already exists in your computer.
Format:
Parameter |
Parameter Prefix |
Specific Input Format |
|
|
The file path must be an absolute file path and include the filename and file extension. |
A filepath specifies a unique location for a file.
Absolute file paths are paths that start with a drive letter (eg. C:\)
|
| If you are using Windows 10, below is a quick way to obtain the file path of the photo you would like to include: |
-
Step 1: Open File Explorer.
-
Step 2: Navigate to the folder that contains the photo you would like to add.
-
Step 3: Select the Photo you would like to add.
-
Step 4: Click on
Copy Pathat the top left corner of the File Explorer window.
Copy Path at the top left corner File Explorer window-
Step 5: Open TravelBuddy and paste the filepath after the parameter prefix
p/.
| TravelBuddy allows for double quotation marks around the filepath, so there is no need to delete them. |
Currently, TravelBuddy supports the following image file formats/extensions:
-
JPEG
.jpg -
PNG
.png -
Bitmap
.bmp
4.4. Listing All Places: list
Description: The list command displays a list of all the places in TravelBuddy.
Shortcut: l
Format: list
4.5. Editing a Place: edit
Description: The edit command edits an existing place in TravelBuddy.
Shortcut: e
Format: edit INDEX [n/NAME] [cc/COUNTRY_CODE] [dv/DATE_VISITED] [r/RATING] [d/DESCRIPTION] [a/ADDRESS] [p/FILE_PATH] [t/TAG]…
Preconditions: Given below is a list of preconditions that must be met for the edit command to work:
-
The command edits the place at the specified
INDEX. The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed place list. The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, … -
It must have at least one of the optional fields.
-
Its existing values will be updated to the input values.
-
The adding of tags is not cumulative. Hence, when the tags are edited, the existing tags of the place will be removed.
-
The tags can all be removed by typing
t/without specifying any tags after it. -
Some parameters have a specific input format.
-
Preconditions for changing the photo file [FILE_PATH] are in Section 4.5.1, “Replacing the photo of a place with
edit p/”
Examples: Given below are some examples on how to utilize the edit command:
-
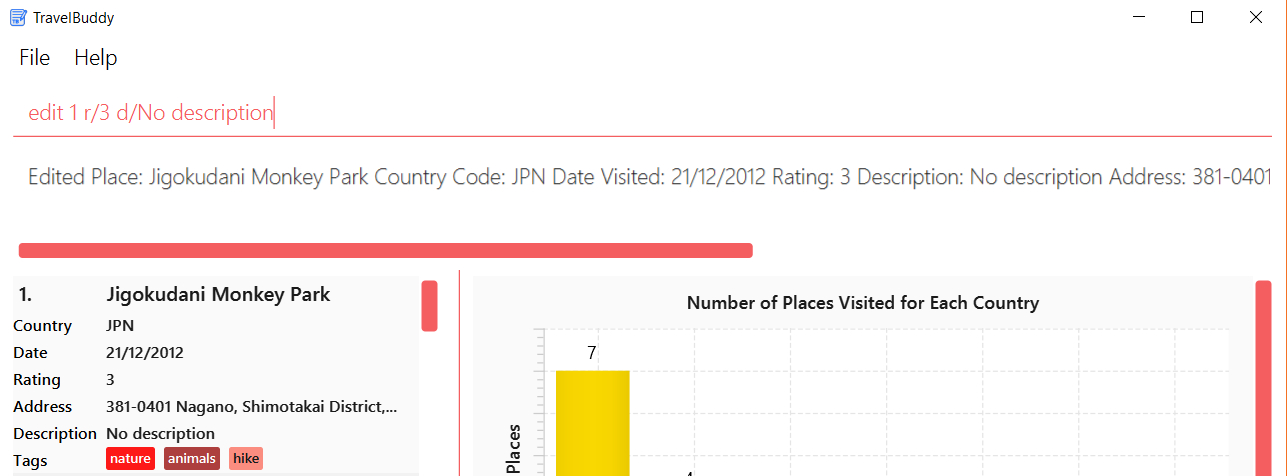
edit 1 r/3 d/No description
Edits the rating and description of the 1st entry in the list to be3andNo descriptionrespectively. -
edit 2 n/Raffles Hotel t/
Edits the name of the 2nd entry in the list to beRaffles Hoteland clears all existing tags.
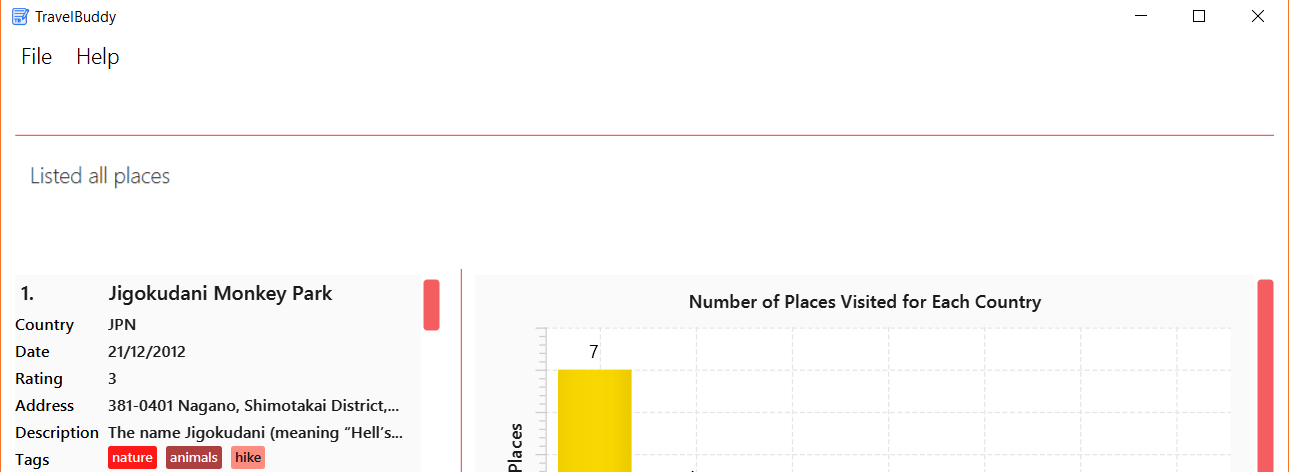
Figure 4.5.1 below shows the list of places before the edit command is used.
edit command is usedFigure 4.5.2 below shows the list of places after the edit command is used.
edit command is used4.5.1. Replacing the photo of a place with edit p/
The edit command can also be used to change the photo of a place by replacing
the FILE_PATH of the current photo with the FILE_PATH of the new photo.
Figure 4.5.1.1 below shows TravelBuddy before edit command is used to replace the current photo.
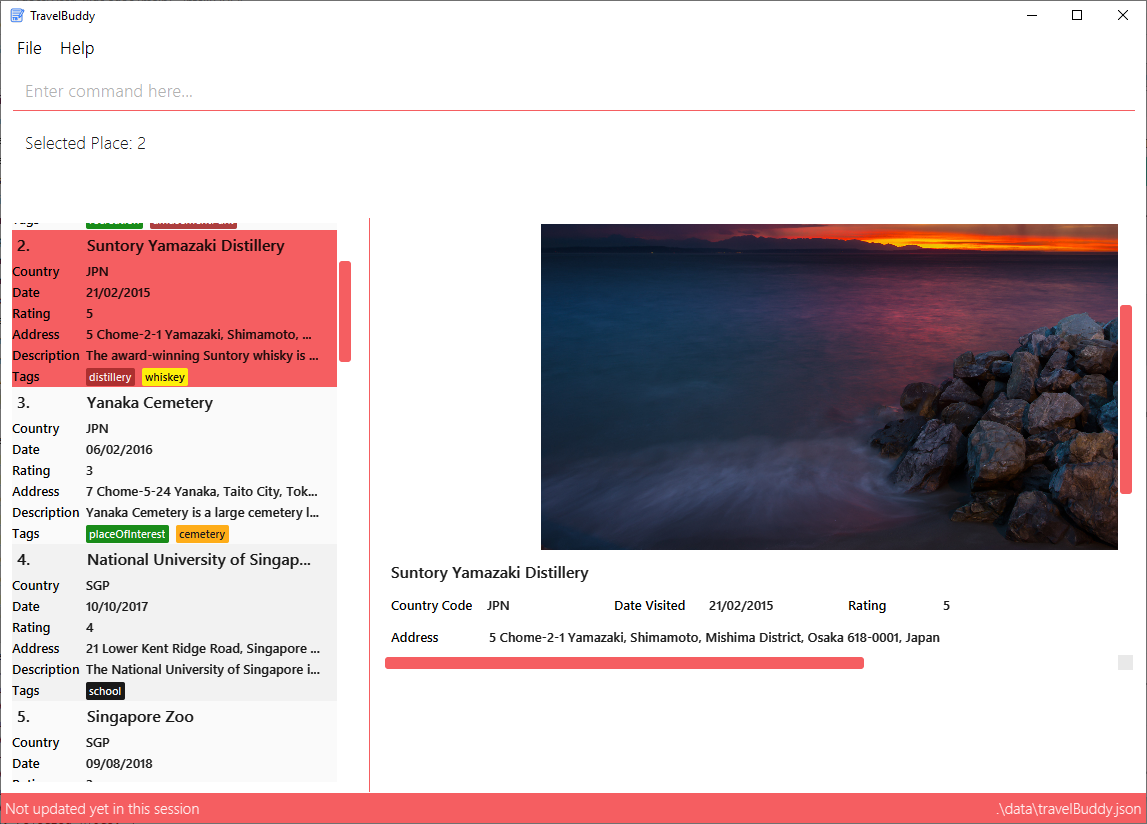
edit command is used to replace a photo.Figure 4.5.1.2 below shows TravelBuddy after a new photo has been added to the place "Suntory Yamazaki Distillery".
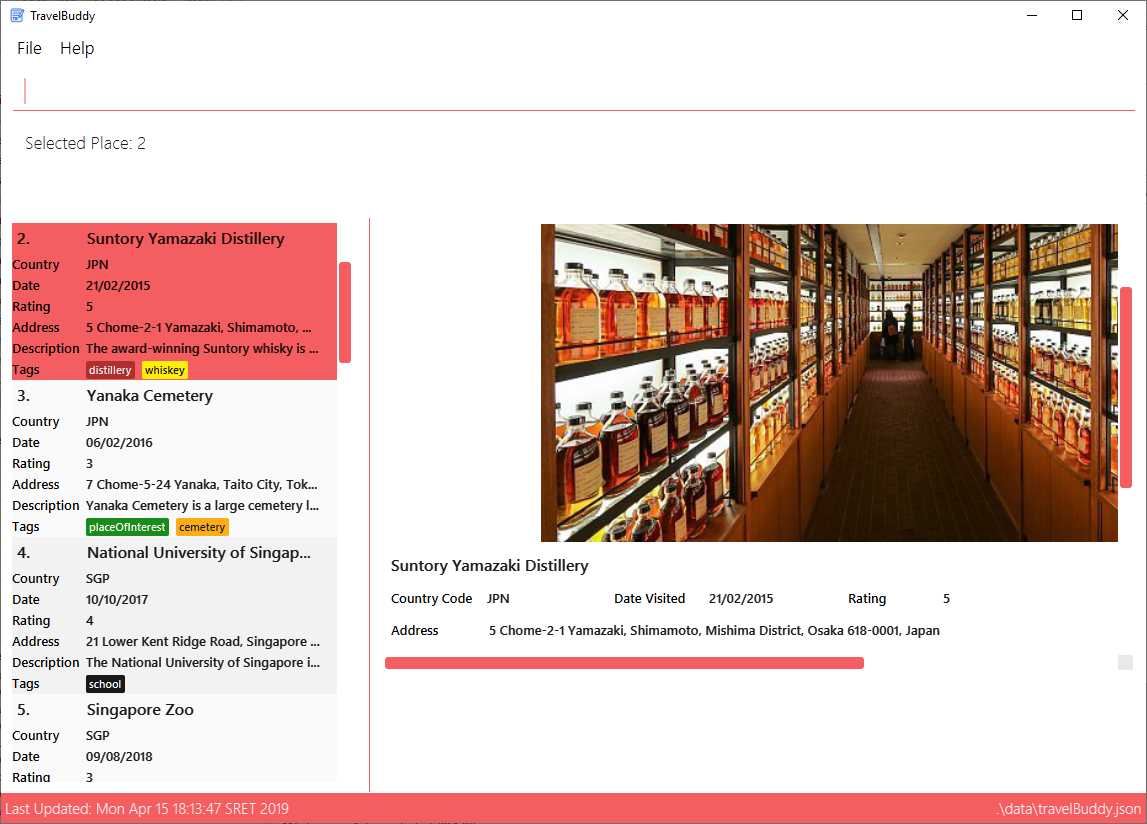
edit command is used to replace a photo.
The image FILE_PATH being replaced with the edit command must still follow the
specifications laid out in Section 4.3.1, “Including a photo when adding a place with p/”
|
4.6. Searching Places by Name: search
Description: The search command searches for places whose names contain any of the given keywords.
Shortcut: se
Format: search KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]
Preconditions: Given below is a list of preconditions that must be met for the search command to work:
-
The search is case insensitive. e.g
nationalwill matchNational. -
The order of the keywords does not matter.
e.g.University National of Singaporewill matchNational University of Singapore. -
Only the name of the places in TravelBuddy is searched.
-
Only full words will be matched.
e.g.Nationwill not matchNational -
Places matching at least one keyword will be returned.
e.g.National Museumwill returnNational Museum of SingaporeandNational University Hospital.
Example: search Singapore
Executes a search for places that contain the keyword Singapore in its name.
From Figure 4.6.1, using search Singapore will return all places in your TravelBuddy that contain Singapore in its name.
In this case, the following are returned as they contain Singapore in their names:
-
Universal Studios Singapore
-
National University of Singapore
-
Singapore Zoo
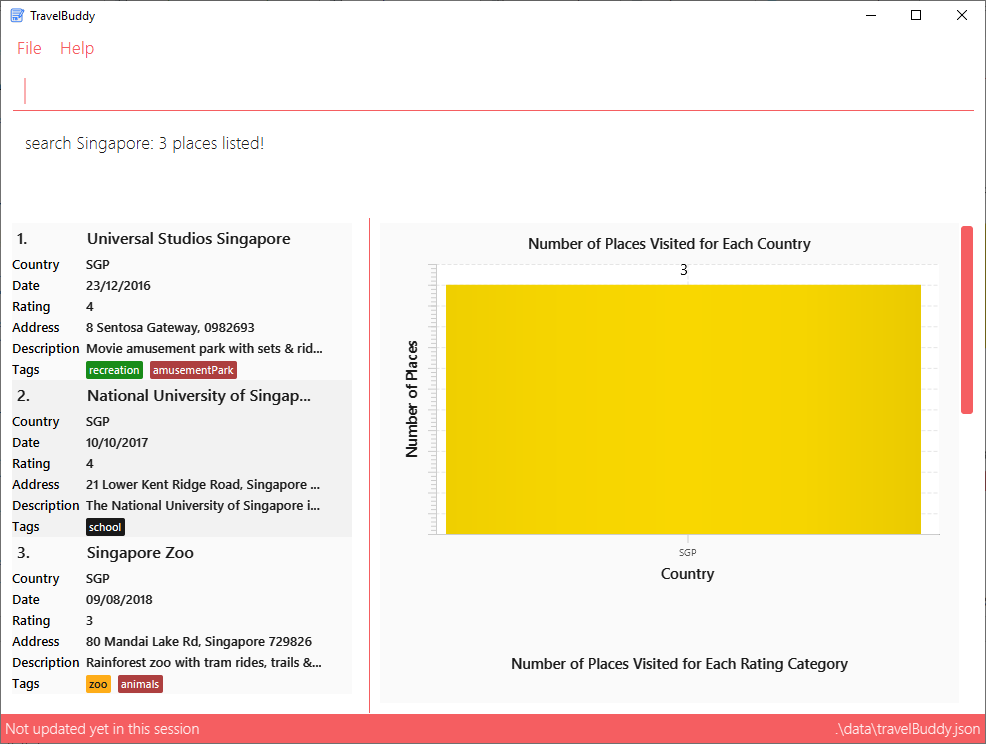
search Singapore4.7. Searching places by Ratings: searchr
Description: The searchr command searches for places whose ratings match the specified rating from 1 to 5.
Shortcut: sr
Format: searchr INDEX [MORE_INDICES]
Preconditions: Given below is a list of preconditions that must be met for the searchr command to work:
-
The rating used in the search must be an integer ranging from 1 to 5.
e.gsearchr 5will return places with 5-star ratings. -
Only the rating of the places in TravelBuddy is searched.
-
Multiple indices can be included in the query, e.g
searchr 4 5will return places with4or5star ratings.
Example: searchr 4
Executes a search for places with a rating of 4.
From Figure 4.7.1 below, using searchr 4 will return all places in your TravelBuddy that have a rating of 4.
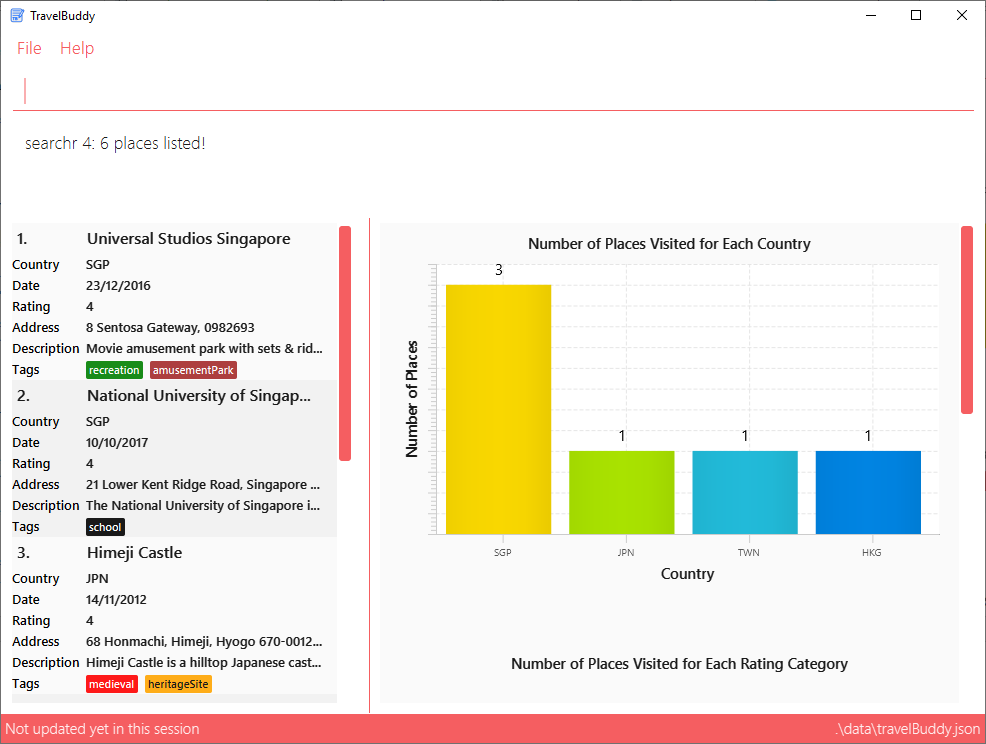
searchr 44.8. Searching Places by Tags: searcht
Description: The searcht command searches for places whose tags correspond to any given keywords.
Shortcut: st
Format: searcht KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]
Preconditions: Given below is a list of preconditions that must be met for the searcht command to work:
-
The search is case insensitive. e.g
Templewill matchtemple. -
Only the tags of the places in TravelBuddy are searched.
-
Only full words will be matched e.g.
tempwill not matchtemple. -
Places tagged with at least one matching keyword will be returned. e.g.
temple schoolwill return places tagged withtempleorschool. -
Multiple keywords can be included in the query, e.g
searcht distillery templewill return places tagged withdistilleryortemple.
Example: searcht distillery
Executes a search for places that are tagged with distillery.
From Figure 4.8.1 below, using searcht distillery will return all places in your TravelBuddy that are tagged with distillery.
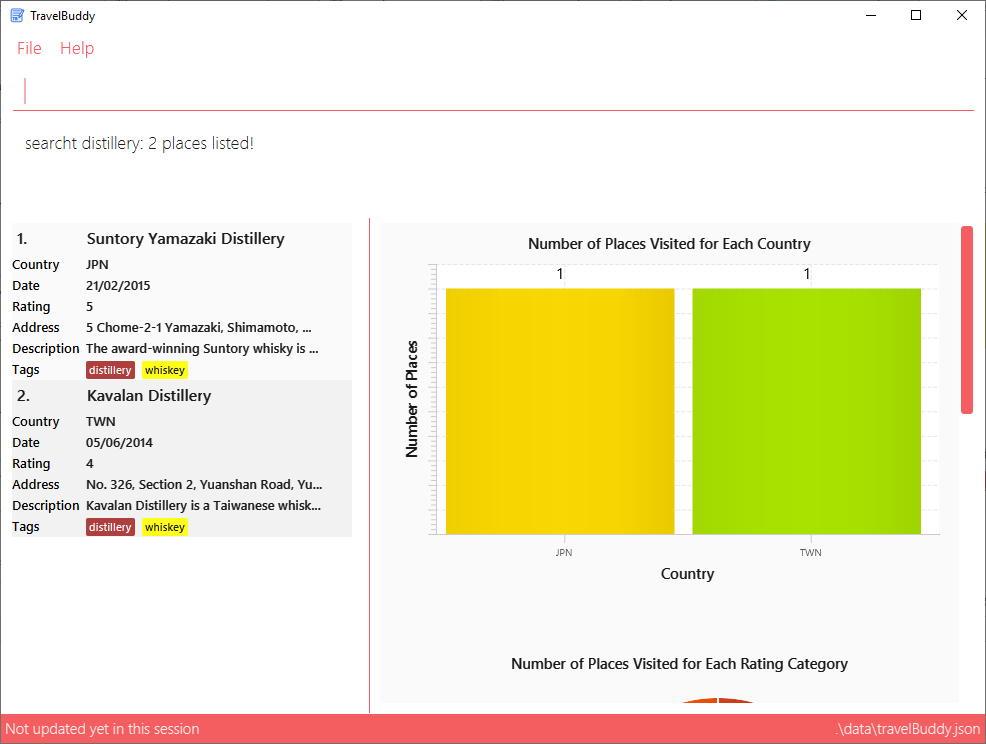
searcht distillery4.9. Searching places by Country: searchc
Description: The searchc command searches for places whose country matches the specified ISO-3166 3-letter country code.
Shortcut: sc
Format: searchc KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]
Preconditions: Given below is a list of preconditions that must be met for the searchc command to work:
-
The country code keywords for
searchcmust be valid 3-letter ISO-3166 country codes. -
The search country is from a list of ISO-3166 country codes. e.g
JPNwill return places located in Japan. -
Only the country of the places in TravelBuddy is searched.
-
Multiple keywords can be included in the query, e.g
searchc JPN CHNwill return places located in Japan or China.
Example: searchc JPN
Executes a search for places located in JPN (Japan).
From Figure 4.9.1 below, using searchc JPN will return all places in your TravelBuddy that are located in Japan.
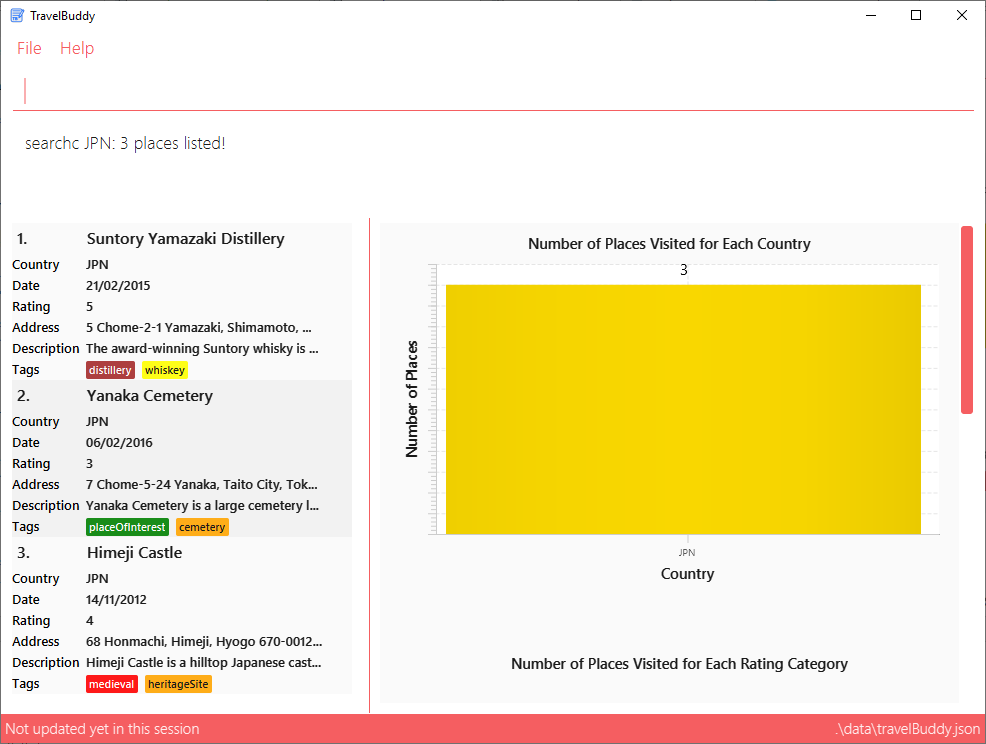
searchc JPN4.10. Searching Places by Year of Visit: searchyear
Description: The searchyear command searches for places whose year of visit matches the specified year of interest.
Shortcut: sy
Format: searchyear KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS] OR searchyear KEYWORD-KEYWORD
Preconditions: Given below is a list of preconditions that must be met for the searchyear command to work:
-
The search year is bounded from 1900 to the current year. e.g
searchyear 2016will return places visited in the year 2016. -
Search requests outside the bounds will issue a warning.
-
The year keywords for
searchyearcan be entered as a range. e.gsearchyear 2010-2017will return all the places visited from 2010 to 2017. -
Only the year of visit of the places in TravelBuddy is searched.
Example: searchyear 2016
Executes a search for places visited in the year 2016.
From Figure 4.10.1 below, using searchyear 2016 will return all places in your TravelBuddy that you visited in the year 2016.
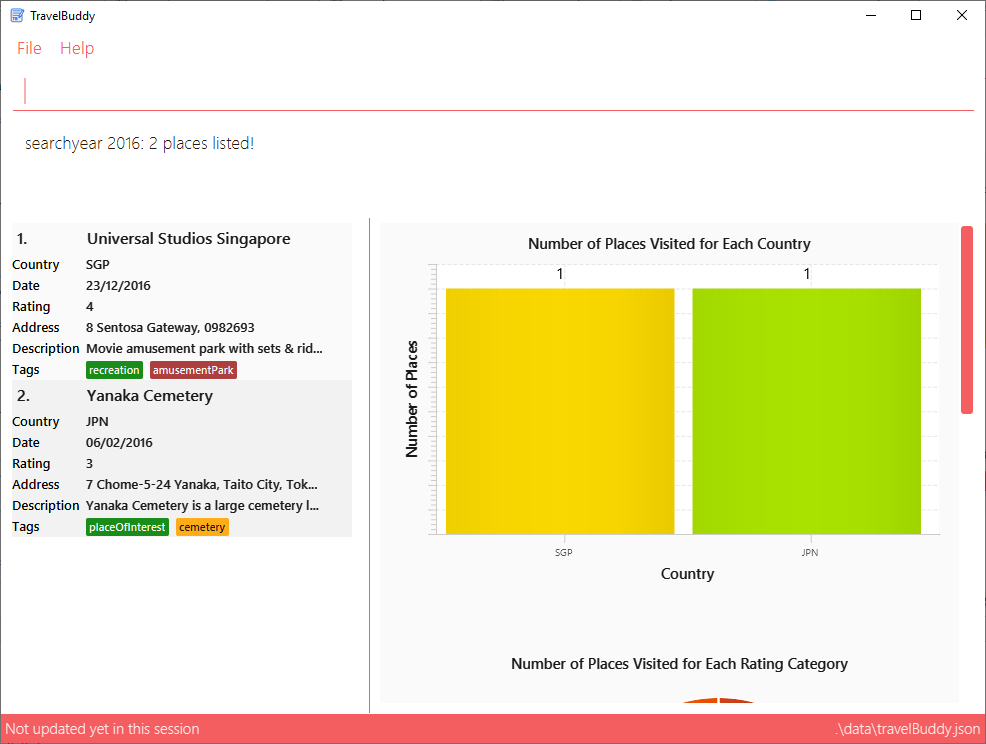
searchyear 20164.11. Deleting a Place: delete
Description: The delete command deletes the specified place from TravelBuddy.
Shortcut: d
Format: delete INDEX
Preconditions: Given below is a list of preconditions that must be met for the delete command to work:
-
Deletes the place at the specified
INDEX. -
The index refers to the index number shown in the currently displayed list, on the left.
-
The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …
Figure 4.11.1 below shows TravelBuddy before delete command is used.
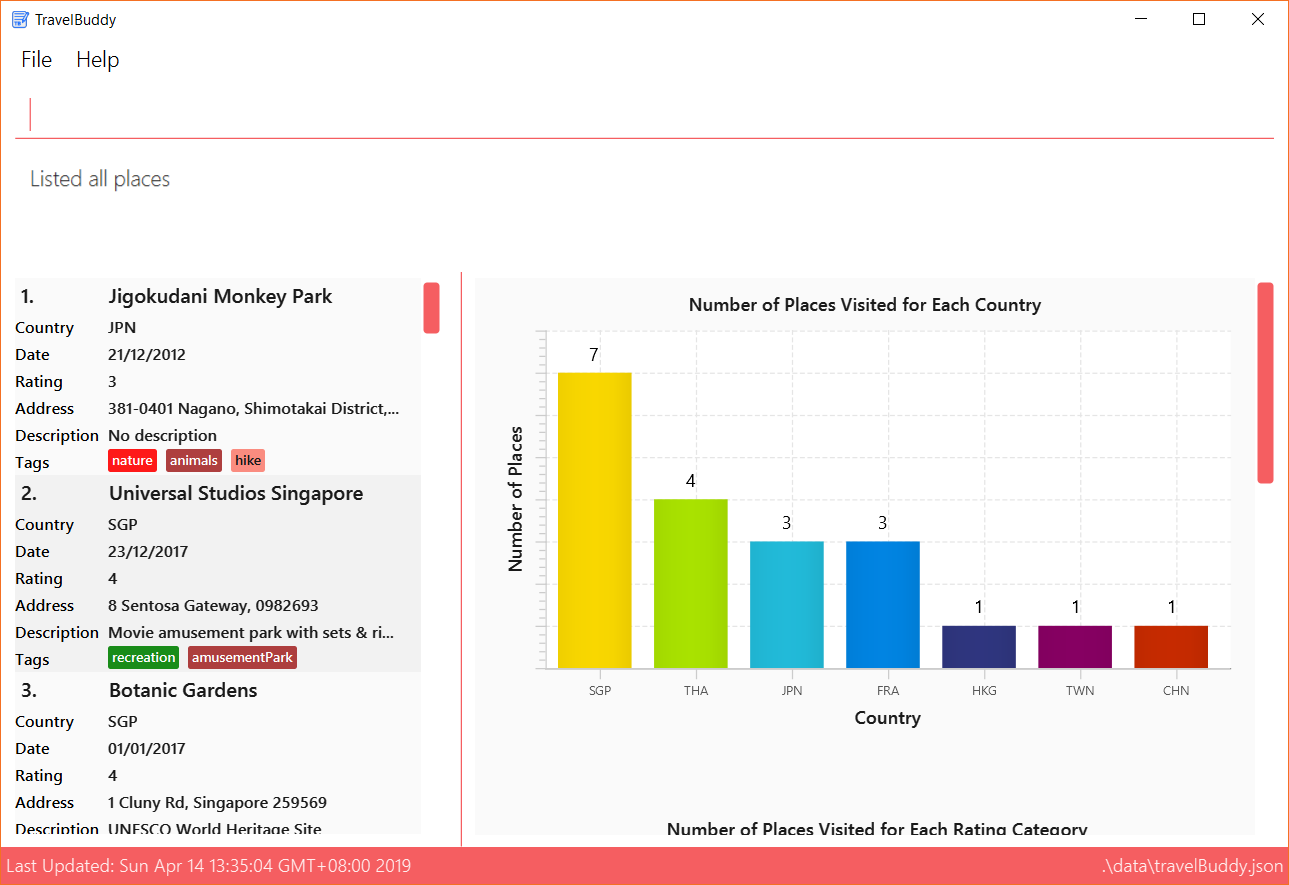
delete command is usedFigure 4.11.2 below shows the result of using the delete command on the first index of the list.
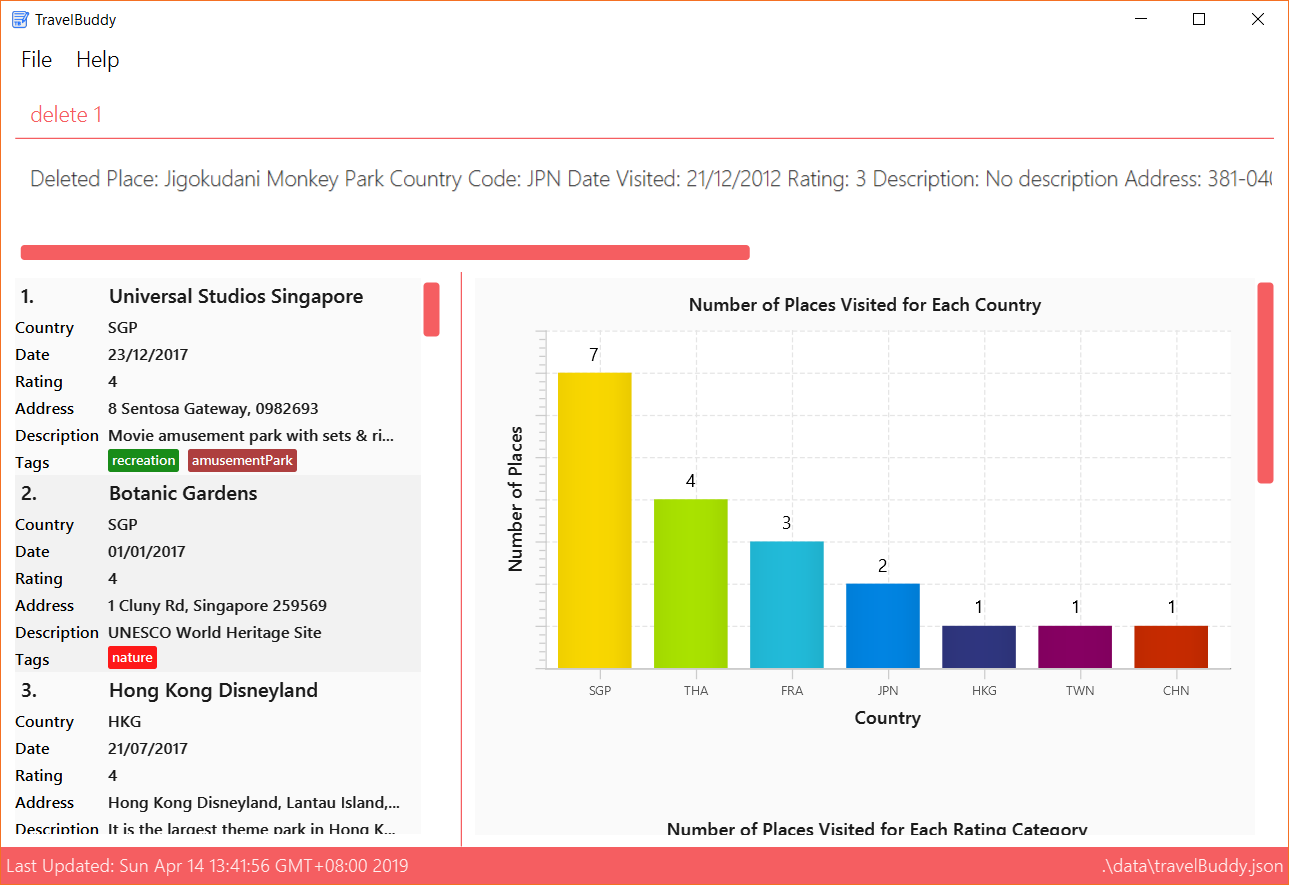
delete command is usedExamples: Given below are some examples on how to utilize the delete command:
-
list
Lists all the places in TravelBuddy.
delete 2
Deletes the 2nd place in TravelBuddy. -
search Raffles
Searches for any places which has the word "Raffles" in it.
delete 1
Deletes the 1st place in the results of thesearchcommand.
4.12. Deleting Multiple Places: deletem
Description: The deletem command deletes multiple places from TravelBuddy’s currently displayed list on the left.
Shortcut: dm
Format: deletem START_INDEX END_INDEX
Preconditions: Given below is a list of precondiitions that must be met for the deletem command to work:
-
Deletes multiple places within a specified range from
START_INDEXtoEND_INDEX. -
START_INDEXmust be smaller than or equal to the last index in the list andEND_INDEX. -
Deletem will delete up till the last entry in TravelBuddy if specified
END_INDEXexceeds the last entry. -
Inclusive of both places specified by
START_INDEXandEND_INDEX. -
The index refers to the index number to the left of each place name, ie. "4. Jalan Kayu".
-
The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …
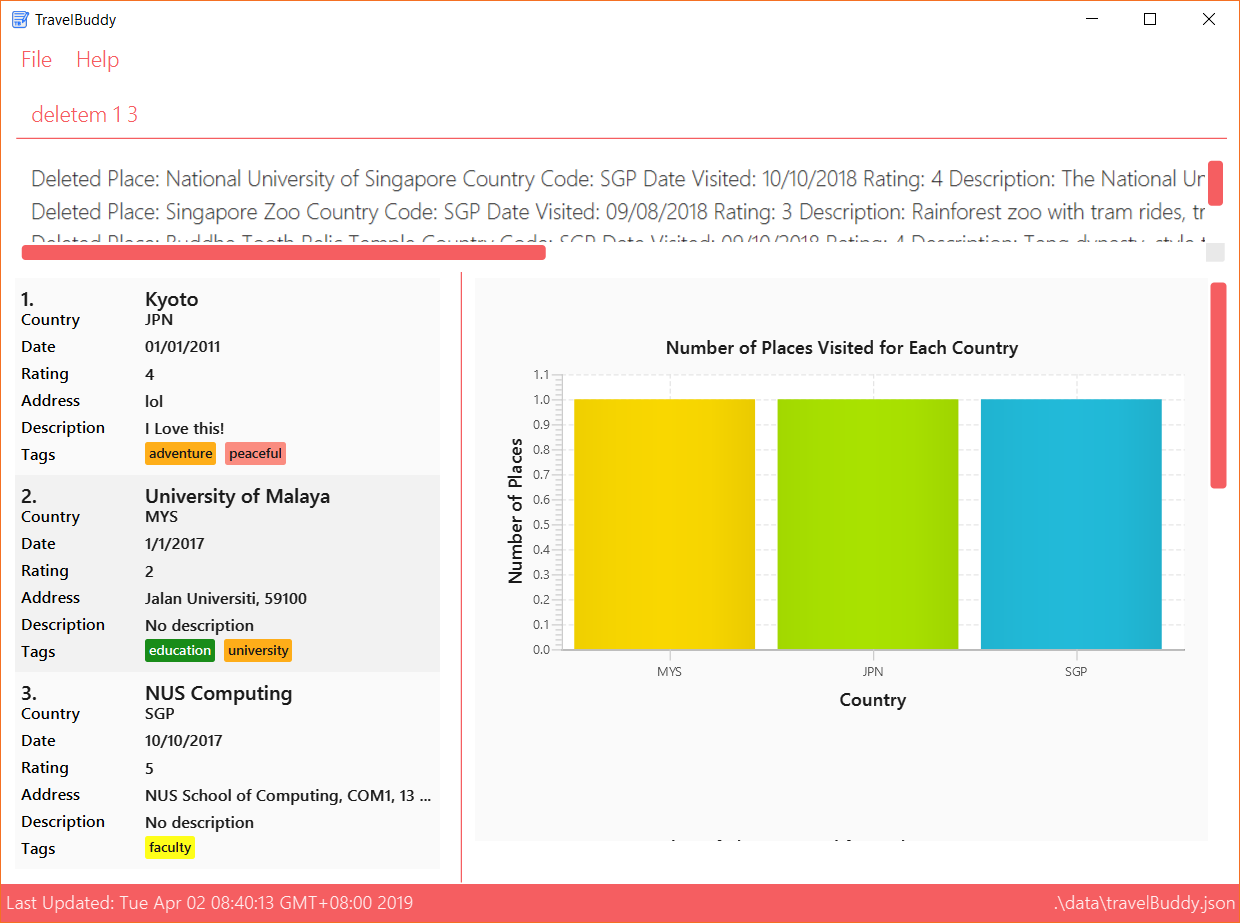
deletem commandExamples: Given below are some examples on how to utilize the deletem command:
-
list
Lists all the places in TravelBuddy.
deletem 1 4
Deletes the 1st, 2nd, 3rd and 4th place in the currently displayed list on the left. -
search Singapore
Searches for any places which has the word "Singapore" in it.
deletem 1 3
Deletes the 1st, 2nd and 3rd place in the results of thesearch Singaporecommand.
4.13. Selecting a Place: select
Description: The select command selects the place identified by the index number used in the currently displayed list on the left,
which loads expanded details of the selected place on the right of the displayed list.
Shortcut: s
Format: select INDEX
Preconditions: Given below is a list of preconditions that must be met for the select command to work:
-
The index refers to the index number to the left of each place name, ie. "4. Jalan Kayu"
-
The index must be a positive integer
1, 2, 3, …
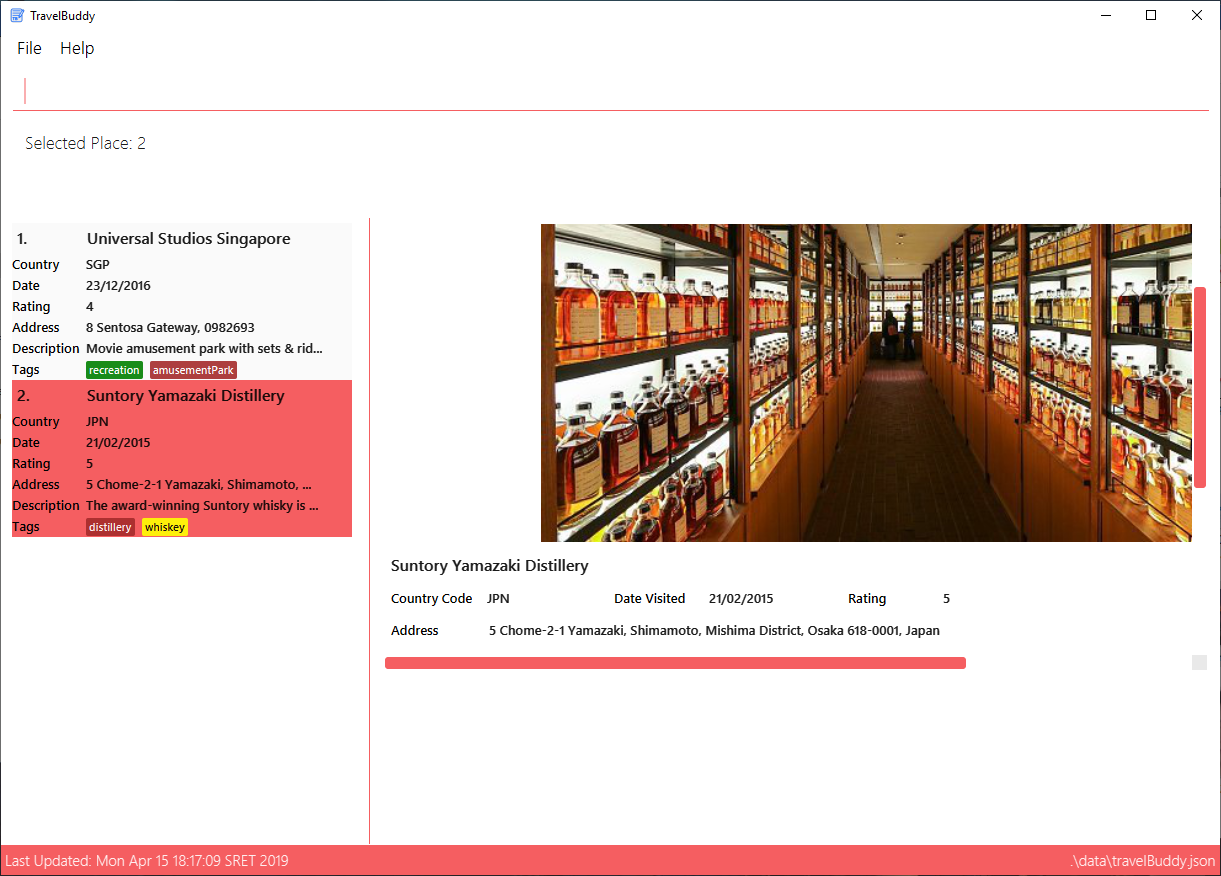
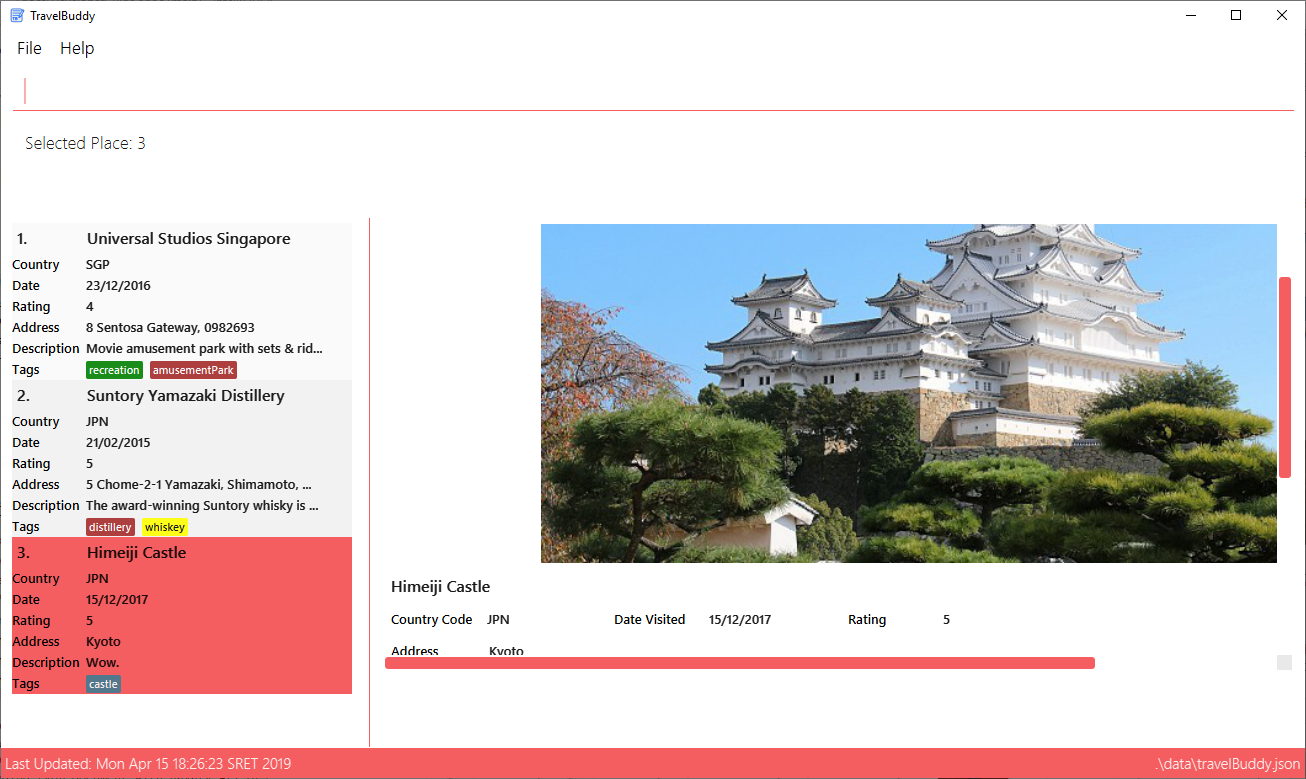
Figure 4.13.1 shows the result of using select 3 command. The place with an index of 2 is highlighted in a red
box and additional information is shown on the right side of the GUI.
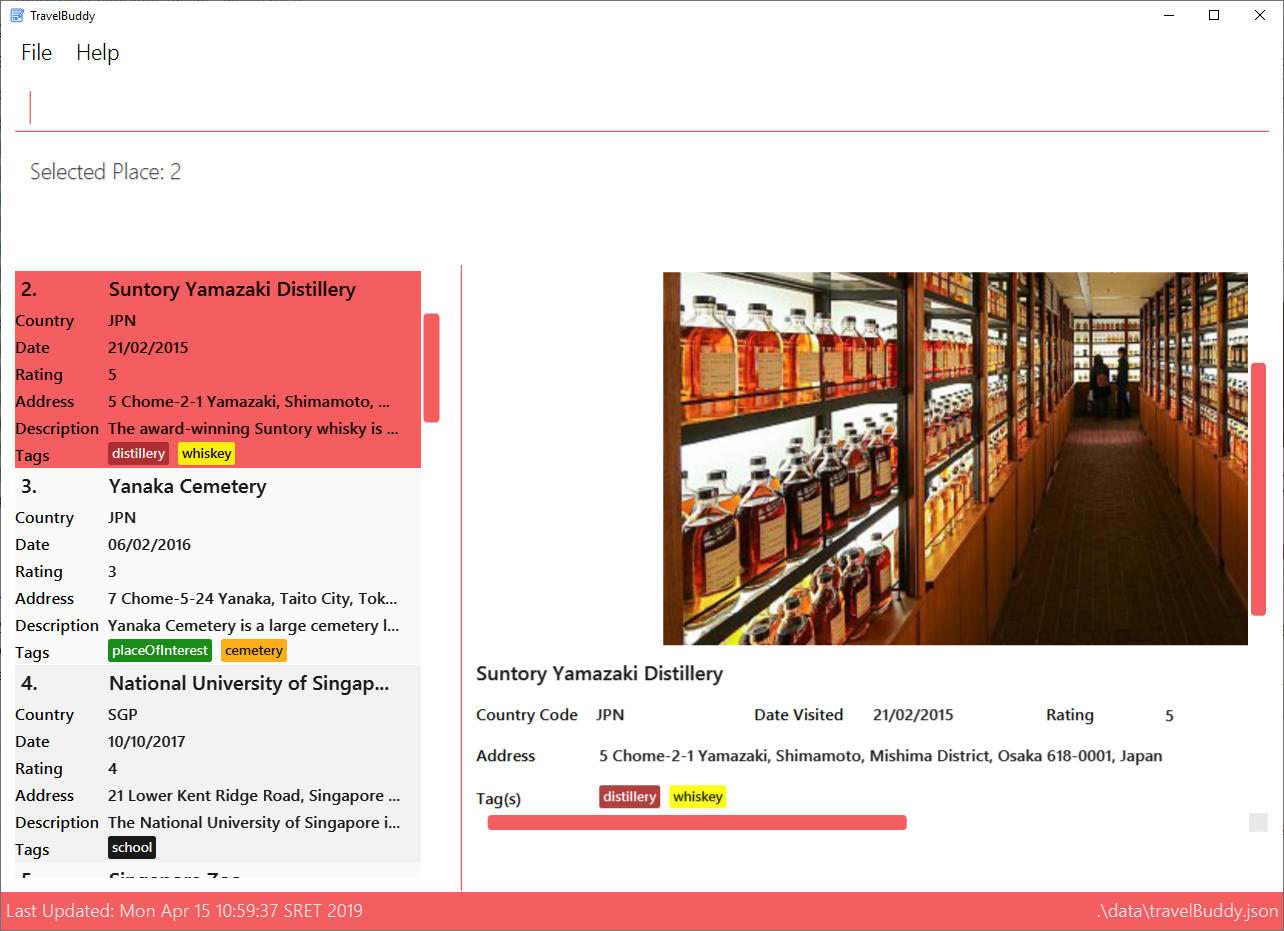
select commandExamples: Given below are some examples on how to utilize the select command:
-
list
Lists all the places in TravelBuddy.
select 2
Selects the 2nd place in TravelBuddy. -
search Raffles
Searches for any places which has the word "Raffles" in it.
select 1
Selects the 1st place in the results of thesearchcommand.
4.14. Listing Previously Entered Commands: history
Description: The history command lists all the commands that you have entered in reverse chronological order.
Shortcut: hi
Format: history
Figure 4.14.1 shows the result of running the history command.

history command|
Pressing the up and down arrows will display the previous and next input respectively in the command box. |
4.15. Undoing Previous Command: undo
Description: The undo command restores TravelBuddy to the state before the previous undoable command was executed.
Shortcut: u
Format: undo
|
Undoable commands: Commands that modify TravelBuddy’s data ( |
Examples: Given below are some examples on how to utilize the undo command:
-
delete 1
Deletes the 1st place on the list currently displayed.
undo
Reverses thedelete 1command. -
select 1
Selects the 1st place on the list currently displayed.
undo
Theundocommand fails as there are no undoable commands executed previously. -
delete 1
Deletes the 1st place on the list currently displayed.
clear
Clears all contents in the list.
undo
Reverses theclearcommand.
undo
Reverses thedelete 1command.
4.16. Redoing the Previously Undone Command: redo
Description: The redo command reverses the most recent undo command.
Shortcut: r
Format: redo
Examples: Given below are some examples on how to utilize the redo command:
-
delete 1
Deletes the 1st place on the list currently displayed.
undo
Reverses thedelete 1command.
redo
Reapplies thedelete 1command. -
delete 1
Deletes the 1st place on the list currently displayed.
redo
Theredocommand fails as there are noundocommands executed previously. -
delete 1
Deletes the 1st place on the list currently displayed.
clear
Clears all contents in the list.
undo
Reverses theclearcommand.
undo
Reverses thedelete 1command.
redo
Reapplies thedelete 1command.
redo
Reapplies theclearcommand.
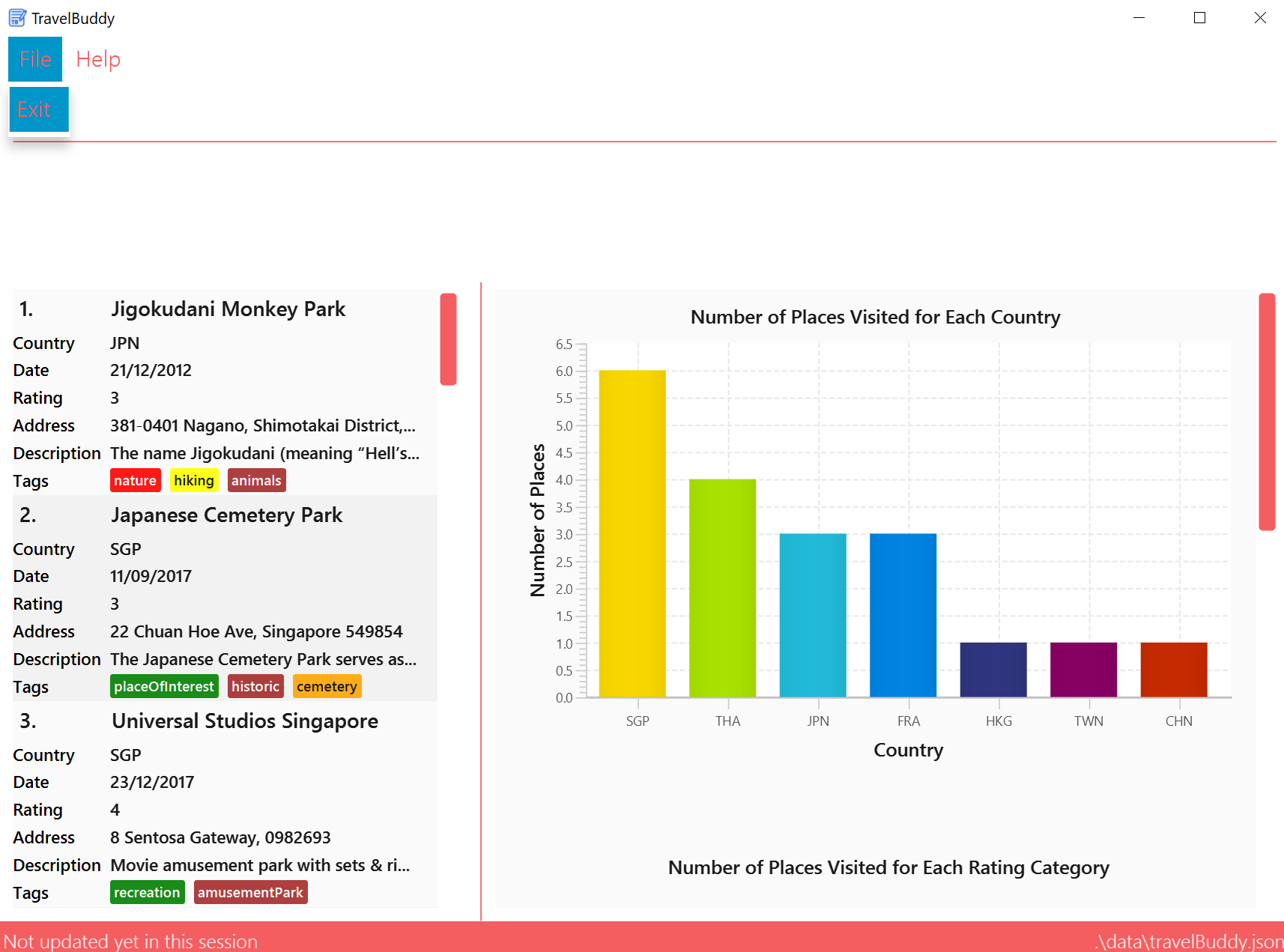
4.17. Generating Charts: generate
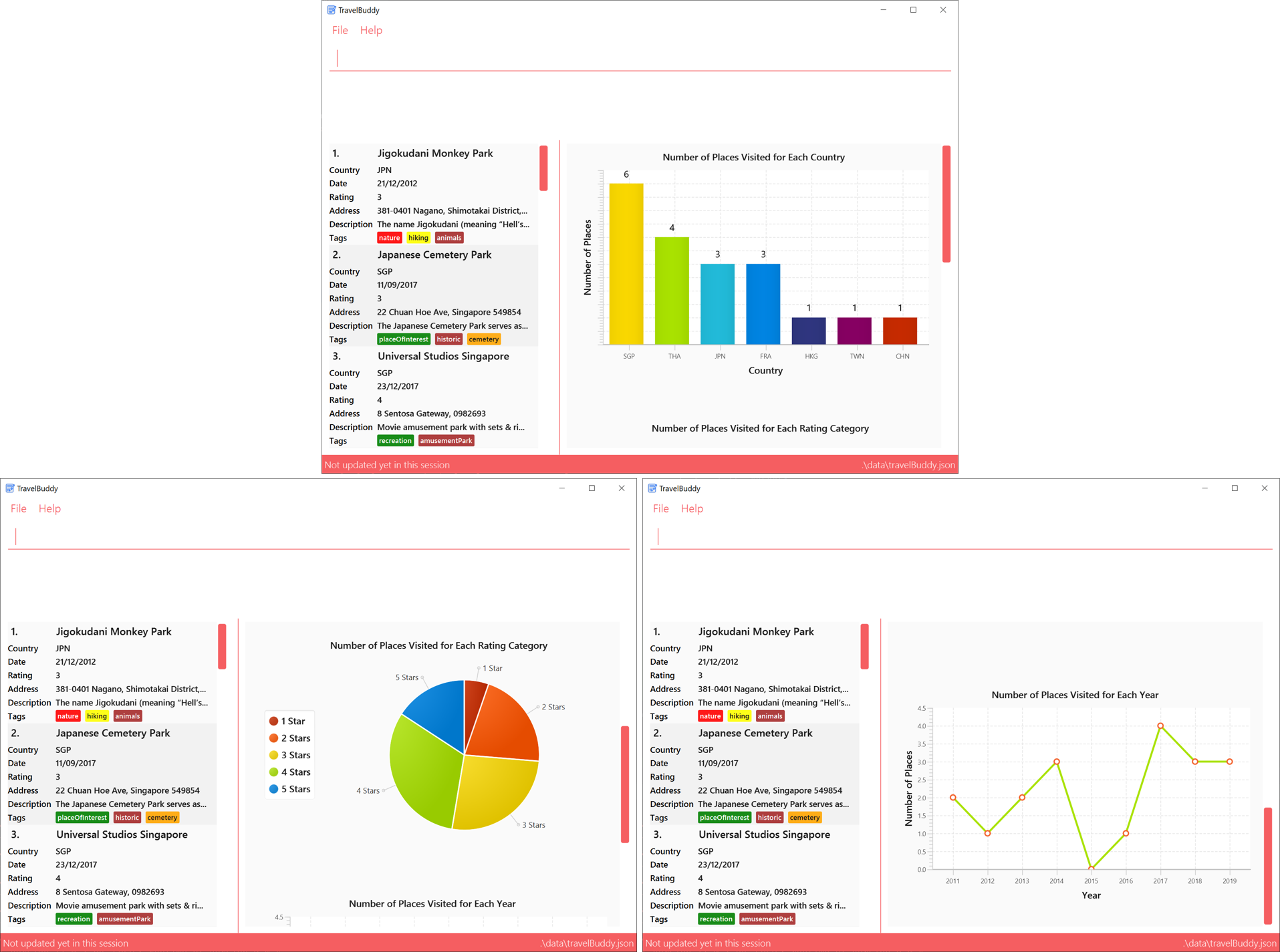
Description: The generate command generates charts based on the list of places in TravelBuddy. TravelBuddy serves up three charts (Figure 4.17.1) that are the most relevant to you as a traveler:
-
The number of places visited for each country
-
The number of places visited for each rating category
-
The number of places visited for each year
Shortcut: g
Format: generate
Preconditions: Given below is a list of preconditions that must be met for the generate command to work:
-
By default, the charts are automatically generated each time TravelBuddy loads.
-
The
generatecommand always triggers the display of all three charts, as seen in Figure 4.17.1. -
The charts always update themselves in real-time.
Example: When a place is added via theaddcommand, the charts are automatically updated so that nogeneratecommand is necessary. -
If the list is empty, the
generatecommand will not display any charts (Figure 4.17.4). -
You can type in any parameters after the
generatecommand, TravelBuddy will simply ignore them (Figure 4.17.2).
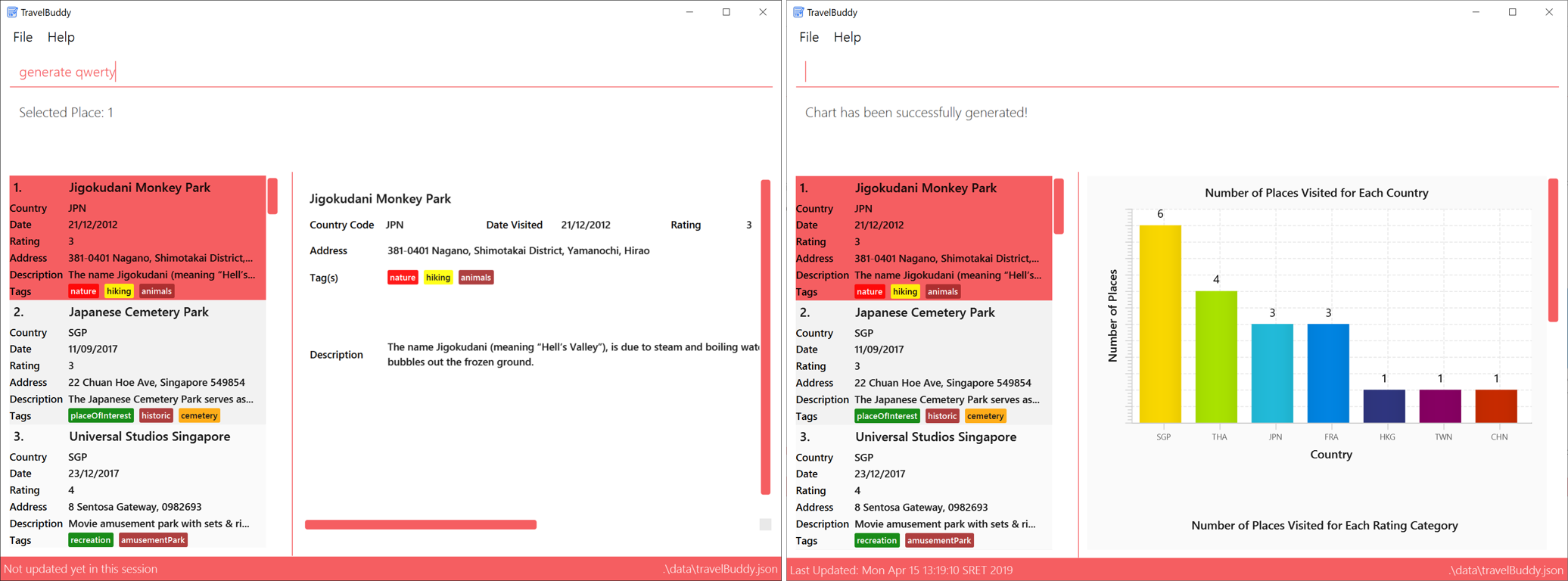
generate commandExamples: Given below are some examples on how to utilize the generate command:
-
select 1
Selects the 1st place in the current list displayed.
generate
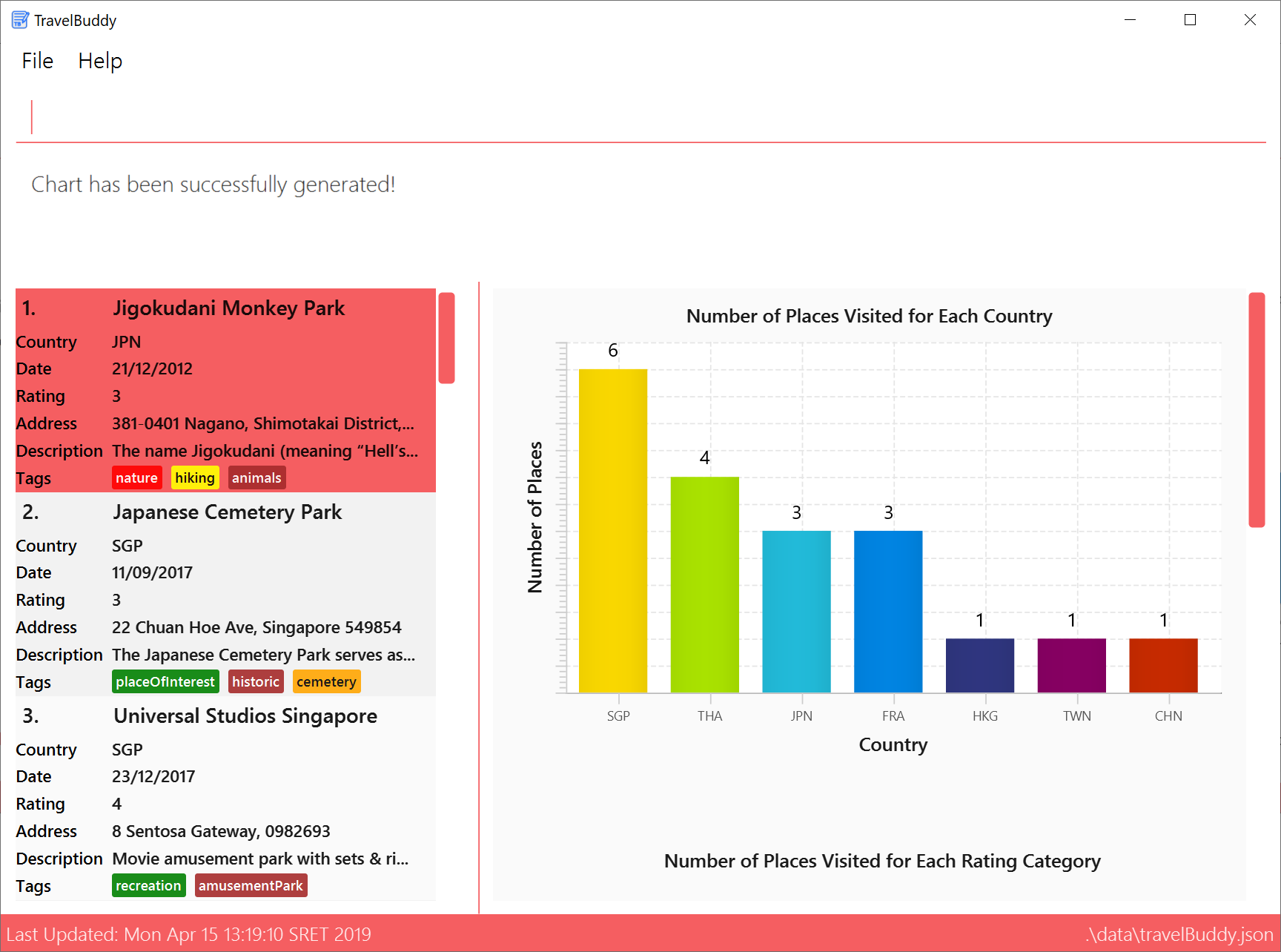
Generates the charts.
Outcome: The charts were successfully generated, as seen in Figure 4.17.3 -
clear
Clears all places in the list.
generate
Generates the charts.
Outcome: Unable to generate the charts as the list is empty, as seen in Figure 4.17.4
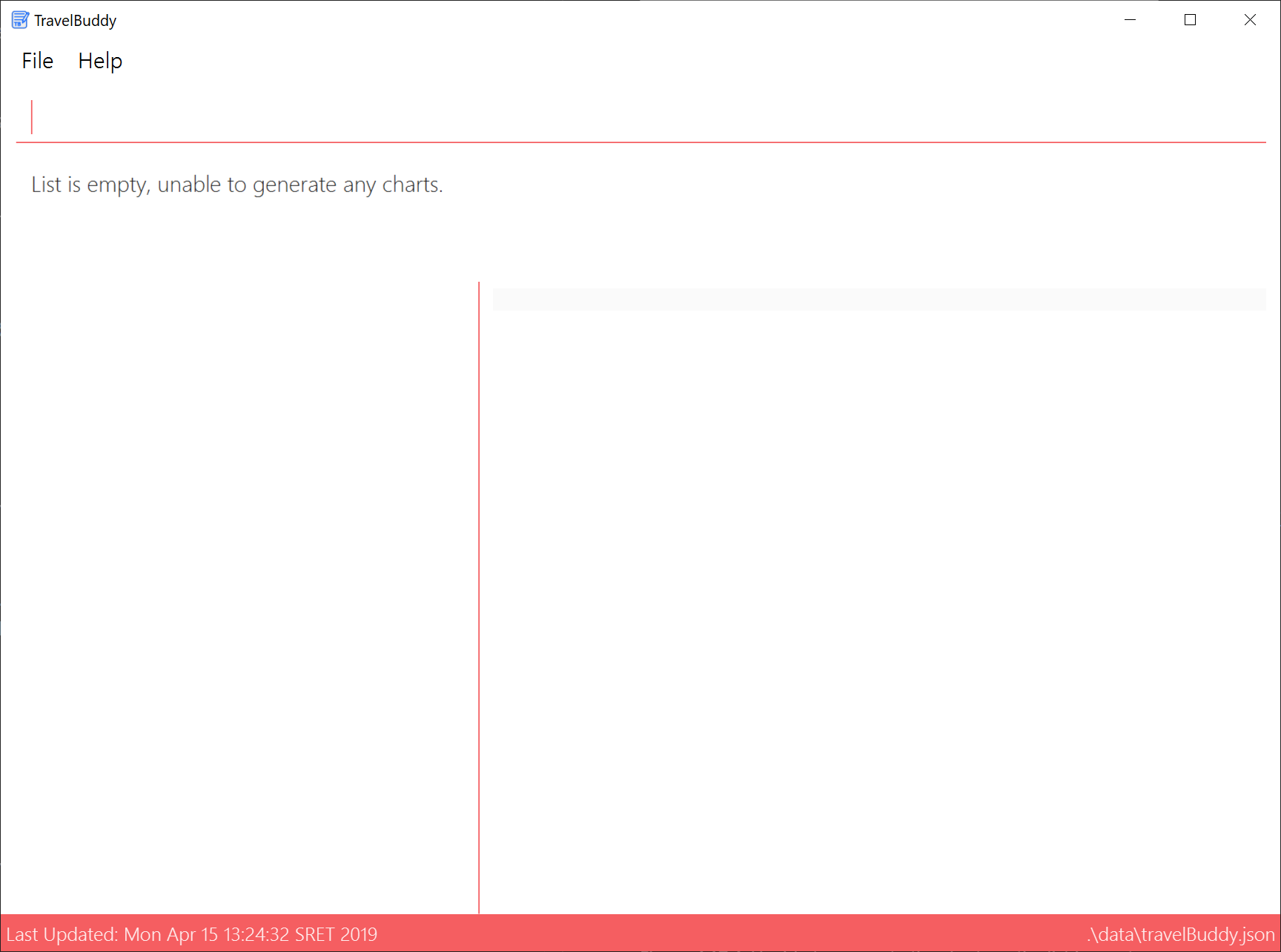
4.18. Clearing All Entries: clear
Description: The clear command clears all place entries from TravelBuddy.
Shortcut: c
Format: clear
Figure 4.18.1 below shows the results of running a clear command, which will remove all places in TravelBuddy.
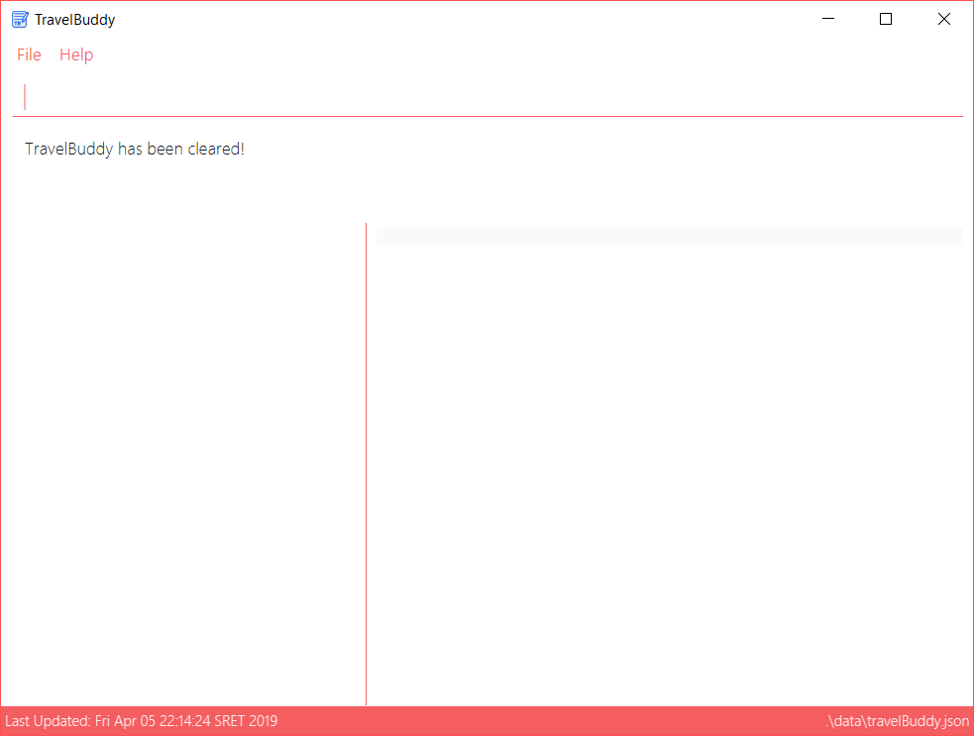
clear command4.19. Exiting the Program: exit
Description: The exit command exits the program.
Shortcut: ex
Format: exit
| An alternative way to exit TravelBuddy is to click FILE > EXIT, as seen in Figure 4.19.1 |
4.20. Saving of Data
TravelBuddy data is saved in the hard disk automatically after any command that changes the data. There is no need to save manually.
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
5.1. Setting Up
Q: Can TravelBuddy be used without an internet connection?
A: Yes, TravelBuddy works without an internet connection.
Q: Why is my TravelBuddy empty?
A: If you are just starting out, TravelBuddy will be empty for you to add places that you have been to.
If you have already added places to TravelBuddy, there is likely an issue with your TravelBuddy.json data file.
Please refer to the section below.
5.2. Data and Storage Issues
Q: How do I transfer my data to another computer?
A: First, install the TravelBuddy on the other computer.
Next, copy the TravelBuddy.json data file from your current TravelBuddy. It is located in the same folder as the TravelBuddy.jar program.
Finally, paste the TravelBuddy.json data file in the folder of your new TravelBuddy.jar program. When a warning box appears with the messages
"There is already a file with the same name in this location.", select "Copy and Replace".
Q: How do I send my TravelBuddy to someone else?
A: You can send the person (via E-mail or messenger applications) your TravelBuddy.json data file. It is located in the same folder as the TravelBuddy.jar program.
Q: Can I reset my TravelBuddy to the state it was when I first launched the application?
A: You can simply repeatedly run the undo command until there are no further commands to undo.
Q: Why is my TravelBuddy empty?
A: If you are just starting out, please refer to Setting Up section. Otherwise, an empty TravelBuddy may mean that your data has been cleared by commands,
or the TravelBuddy.json data file is missing or corrupted.
Please check that the file is located in the same folder as the TravelBuddy.jar program executable, and
the file can be opened by a text editor such as NotePad.
5.3. Command Issues
Q: How do I view the full TravelBuddy after searching or selecting an entry?
A: You can use the command list to retrieve the full TravelBuddy.
Q: What details do I need for the add command?
A: The following details are required for a valid add command:
-
Name of the place (Prefix:
n/) -
Country code of the place (Prefix:
cc/) -
Date the place was visited (Prefix:
dv/) -
Rating of the place (Prefix:
r/) -
Description of the place (Prefix:
d/) -
Address of the place (Prefix:
a/)
Q: What details are optional for the add command?
A: The following details are optional for a valid add command:
-
Tags of the place (Prefix:
t/) -
Filepath of the photo file for the place (Prefix:
p/)
Q: Why does the undo command not work?
A: The undo command only reverses the commands add, delete, deletem, generate, edit and clear.
Q: Why does the undo command reverse a command from multiple commands before?
A: The undo command reverses the last used add, delete, deletem, edit, generate and clear command.
6. Cheatsheet
6.1. Command Glossary and Shortcuts
Below is a summarized list of all the command glossary and shortcuts that TravelBuddy supports:
Command |
Shortcut |
Explanation |
Add |
|
Adds a place to TravelBuddy. |
Clear |
|
Clears all place entries from TravelBuddy. |
Delete |
|
Deletes the specified place from TravelBuddy. |
Delete Multiple |
|
Deletes multiple places from TravelBuddy’s currently displayed list on the left. |
Edit |
|
Edits an existing place in TravelBuddy. |
Exit |
|
Exits the program. |
Generate |
|
Generates charts based on the list of places in TravelBuddy. |
Help |
|
Opens up a help page. |
History |
|
Lists all the commands that you have entered in reverse chronological order. |
List |
|
Lists all the places in TravelBuddy. |
Redo |
|
Reverses the most recent undo command. |
Search |
|
Searches for places whose names contain any of the given keywords. |
Search Country |
|
Searches for places whose country matches the specified ISO-3166 3-letter country code. |
Search Rating |
|
Searches for places whose ratings match the specified rating from 1 to 5. |
Search Tags |
|
Searches for places whose tags correspond to any given keywords. |
Search Year |
|
Searches for places whose year of visit matches the specified year of interest. |
Select |
|
Selects the place identified by the index number used in the currently displayed list on the left, which loads expanded details of the selected place on the right of the displayed list. |
Undo |
|
Restores TravelBuddy to the state before the previous undoable command was executed. |
6.2. Command Formats
Below is a summarized list of all the command formats that TravelBuddy supports:
Command |
Format |
Add |
Example: |
Clear |
|
Delete |
Example: |
Delete Multiple |
Example: |
Edit |
Example: |
Exit |
|
Generate |
|
Help |
|
History |
|
List |
|
Redo |
|
Search |
Example: |
Search Country |
Example: |
Search Rating |
Example: |
Search Tags |
Example: |
Search Year |
Examples: |
Select |
Example: |
Undo |
|